Product Description
Stainless Steel Endless Screw Worm / Worm gear
1. Description
| No. | Item | Description |
| 1 | Name | Worm |
| 2 | Size | Products can be customized. |
| 3 | Material | 45#Steel,20CrMnTi,40Cr,20CrNiMo,20MnCr5,GCR15SiMn,42CrMo,2Cr13stainless steel,Nylon,Bakelite,Copper,Aluminium.etc |
| 4 | Production Process | The main process is Gear Milling and Gear Grinding, Selecting production process according to the different products. |
| 5 | Heat Treatment | Selecting heat treatment according to the different materials. |
| 6 | Testing Equipment | Rockwell hardness tester 500RA, Double mesh instrument HD-200B & 3102,Gear measurement center instrument CNC3906T and other High precision detection equipments |
| 7 | Certification | GB/T19001-2016/ISO9001:2015 |
| 8 | Usage | Used in printing machine, cleaning machine, medical equipment, garden machine, construction machine, electric car, valve, forklift, transportation equipment and various gear reducers.etc |
| 9 | Package | According to customer’s request |
2. Photos
3. Order process
a. Customer sends us the drawing or sample, If only sample, our company supply the CAD drawing.
b. Our company supplies the processing technique and quotation.
c. Our company supplies the sample after customer confirmed processing technique and quotation.
d. Customer places the order after confirm the sample.
e. Customer pay 50% deposit
f. Quantity production.
g. Pay the balance after the acceptance and confirmation.
h. Delivery.
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Gear Milling and Gear Grinding |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Involute |
| Material: | 45#Steel,20crmnti,40cr,20CrNiMo,20mncr5,Gcr15simn, |
| Samples: |
US$ 35/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
What is the purpose of using screw gears in machinery?
Screw gears, also known as worm gears, serve various purposes in machinery and mechanical systems. They offer unique advantages that make them suitable for specific applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purposes and benefits of using screw gears:
- High Gear Reduction: One of the primary purposes of using screw gears is to achieve high gear reduction. Screw gears provide a significant reduction ratio, allowing for the conversion of high-speed, low-torque input to low-speed, high-torque output. This makes them ideal for applications that require precise control over torque and rotational speed, such as lifting heavy loads, positioning systems, and machinery with high torque requirements.
- Precise Positioning: Screw gears enable precise positioning and control of linear or rotary motion. The fine-pitch threads on the worm and the corresponding worm wheel teeth allow for accurate and controlled motion. This feature makes screw gears suitable for applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics, automation, and machinery that performs intricate movements or adjustments.
- Self-Locking: Screw gears have a self-locking property, which means that the gear mechanism remains fixed in position even when no external force is applied. The friction between the screw threads and the worm wheel prevents the system from backdriving or rotating unintentionally. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locks, making screw gears advantageous in applications where holding a position is essential for safety and stability.
- Compact Design: Screw gears have a compact design that makes them suitable for applications with limited space. The worm and worm wheel arrangement allows for efficient power transmission in a compact layout, enabling the integration of screw gears in machinery and systems where space is a constraint. This compact design also simplifies installation and reduces the overall footprint of the equipment.
- Quiet and Smooth Operation: Screw gears operate with reduced noise and vibration compared to other gear types. The helical nature of the threads and the sliding/rolling contact between the worm and worm wheel result in a smooth and gradual meshing motion. This smooth operation contributes to quieter machinery, making screw gears desirable in applications where noise reduction is important, such as in residential environments, audio equipment, and precision instruments.
- High Shock Load Resistance: Screw gears are known for their ability to handle shock loads effectively. The helical shape of the threads and the larger contact area between the worm and the worm wheel distribute the load more evenly, reducing the risk of sudden failures or damage due to shock or impact loads. This shock load resistance makes screw gears suitable for applications that involve sudden changes in load or external forces.
- Reliability and Durability: Screw gears are recognized for their reliability and durability. The simplicity of their design, with fewer moving parts, reduces the likelihood of mechanical failures. Additionally, the self-locking feature minimizes the chances of unwanted movement or slippage. When properly lubricated and maintained, screw gears can have a long service life and require minimal maintenance, contributing to the overall reliability of machinery.
- Wide Range of Applications: Screw gears find application in various industries and machinery types. They are utilized in manufacturing equipment, robotics, medical devices, automotive systems, elevators, material handling machinery, and many other systems that require precise control, high torque, compactness, and reliable power transmission.
The purpose of using screw gears in machinery is to provide efficient power transmission, precise positioning, high torque multiplication, self-locking capabilities, and reliable operation. These features make screw gears a valuable component in numerous applications, enhancing performance, safety, and overall functionality of machinery and mechanical systems.

How do you calculate the efficiency of a screw gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a screw gear, also known as a worm gear, involves determining the ratio of input power to output power and considering various factors that affect the overall efficiency of the gear system. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to calculate the efficiency of a screw gear:
- Measure Input Power: The first step is to measure or determine the input power to the screw gear system. This can be done by measuring the torque applied to the input shaft and the rotational speed of the input shaft. The input power can then be calculated using the formula: Input Power (Pin) = Torque (Tin) × Angular Speed (ωin).
- Measure Output Power: Next, measure or determine the output power of the screw gear system. This can be done by measuring the torque exerted by the output shaft and the rotational speed of the output shaft. The output power can be calculated using the formula: Output Power (Pout) = Torque (Tout) × Angular Speed (ωout).
- Calculate Mechanical Efficiency: The mechanical efficiency of the screw gear system is calculated by dividing the output power by the input power and multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula for mechanical efficiency is: Mechanical Efficiency = (Pout/Pin) × 100%.
- Consider Efficiency Factors: It’s important to note that the mechanical efficiency calculated in the previous step represents the ideal efficiency of the screw gear system, assuming perfect conditions. However, several factors can affect the actual efficiency of the system. These factors include friction losses, lubrication efficiency, manufacturing tolerances, and wear. To obtain a more accurate assessment of the overall efficiency, these factors should be considered and accounted for in the calculations.
- Account for Friction Losses: Friction losses occur in screw gear systems due to the sliding contact between the worm gear and the worm wheel. To account for friction losses, a correction factor can be applied to the calculated mechanical efficiency. This correction factor is typically determined based on empirical data or manufacturer specifications and is subtracted from the mechanical efficiency to obtain the corrected efficiency.
- Consider Lubrication Efficiency: Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and improving the efficiency of screw gear systems. In practice, the lubrication efficiency can vary depending on factors such as the type of lubricant used, the lubrication method, and the operating conditions. To account for lubrication efficiency, a lubrication factor can be applied to the corrected efficiency calculated in the previous step. This factor is typically determined based on experience or manufacturer recommendations.
- Include Other Efficiency Factors: Depending on the specific application and the characteristics of the screw gear system, additional efficiency factors may need to be considered. These factors can include manufacturing tolerances, gear wear, misalignment, and other losses that can affect the overall efficiency. It’s important to assess these factors and apply appropriate correction factors or adjustments to the efficiency calculation.
By following these steps and considering the various factors that affect the efficiency of a screw gear system, it is possible to calculate a more accurate estimate of the gear’s efficiency. Keep in mind that the calculated efficiency is an approximation, and actual efficiency can vary based on operating conditions, maintenance practices, and other factors specific to the gear system and application.

Are there different types of screw gears available?
Yes, there are different types of screw gears available, each with its variations in design and functionality. These variations cater to specific applications and requirements. Here are some of the commonly used types of screw gears:
- Single-Thread Worm Gears: Single-thread worm gears have a single helical thread on the worm. They provide a relatively higher gear ratio and are commonly used in applications requiring moderate torque and precision positioning. Single-thread worm gears are widely employed in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and machinery.
- Multi-Thread Worm Gears: Multi-thread worm gears have multiple helical threads on the worm, typically two or more. The presence of multiple threads increases the contact area and allows for higher torque transmission. Multi-thread worm gears offer higher gear reduction ratios and are suitable for applications requiring greater torque multiplication, such as heavy-duty machinery and high-load lifting systems.
- Fine-Pitch Worm Gears: Fine-pitch worm gears have a smaller pitch, meaning there are more teeth per unit length of the worm. This design allows for finer control and precise positioning. Fine-pitch worm gears find applications in industries where accurate motion control is critical, such as robotics, automation, and optics.
- Coarse-Pitch Worm Gears: Coarse-pitch worm gears have a larger pitch, resulting in fewer teeth per unit length of the worm. This design provides higher torque transmission and is suitable for applications requiring heavy-duty power transmission. Coarse-pitch worm gears are commonly used in industries like manufacturing, material handling, and conveyors.
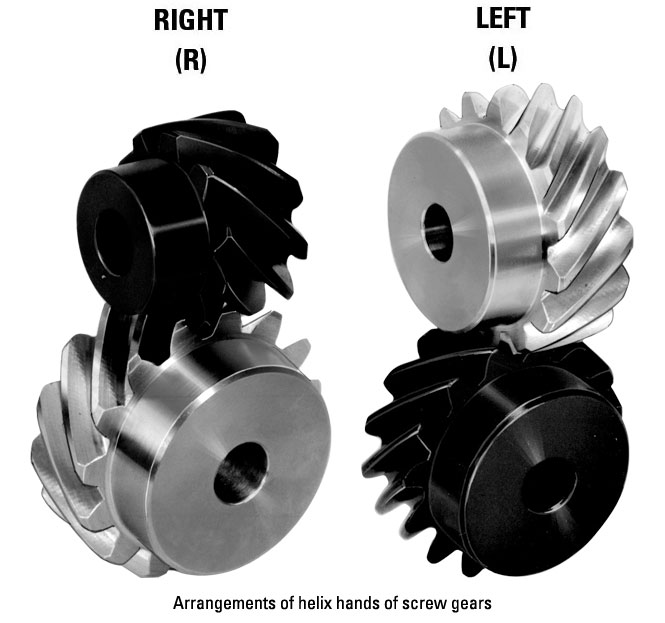
- Right-Handed and Left-Handed Worm Gears: Screw gears can be classified as right-handed or left-handed based on the direction of the helical thread. In a right-handed worm gear, the helical thread advances in a clockwise direction when viewed from the end of the worm. In a left-handed worm gear, the helical thread advances counterclockwise. The choice between right-handed and left-handed worm gears depends on the specific application and the desired rotational direction.
- Non-Throated and Throated Worm Gears: Non-throated worm gears have a cylindrical worm without a groove, while throated worm gears have a groove or a notch on the worm. The presence of a throat allows for greater contact between the worm and the worm wheel, increasing the gear meshing efficiency and load-carrying capacity. Throated worm gears are commonly used in applications where higher efficiency and load capacity are required.
- Self-Locking Worm Gears: Self-locking worm gears are designed to have a high self-locking capability. The helical thread angle and the friction between the worm and the worm wheel prevent the worm wheel from backdriving the worm when the system is at rest. Self-locking worm gears are widely used in applications that require holding a position without the need for additional braking or locking mechanisms, such as elevators, lifts, and positioning systems.
These are some of the different types of screw gears available in the market. The selection of a specific type depends on factors such as torque requirements, gear reduction ratio, precision positioning, load capacity, and self-locking capabilities, among others. Understanding the characteristics and variations of screw gears allows for choosing the most suitable type for a given application.


editor by CX 2023-11-01